SIC 3317
STEEL PIPE AND TUBES
Included in this category are establishments primarily engaged in the production of welded or seamless steel pipe and tubes and heavy riveted steel pipe from purchased materials. Establishments primarily engaged in the production of steel, including steel skelp or steel blanks, tube rounds, or pierced billets, are classified under SIC 3312: Blast Furnaces & Steel Mills.
NAICS Code(s)
331210 (Iron and Steel Pipes and Tubes Manufacturing from Purchased Steel)
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, more than 325 establishments operated in this category at the onset of the twenty-first century. Industry-wide employment totaled 27,180 workers receiving a payroll of more than one billion dollars. Within this workforce, 21,502 of these employees worked in production, putting in almost 45 million hours to earn wages of more than $715 million. Overall shipments for the industry were valued at almost $7.8 billion.
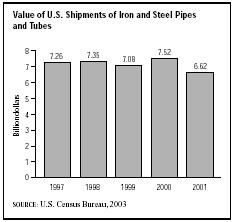
After some years of declining sales, the American steel pipe and tubes industry entered a period of stronger economic growth in the mid-1990s. Total shipments were $6.3 billion in 1996, up almost 6 percent from the 1994 level of six billion. Rising demand, the increasing price of raw material, and energy costs drove the prices of seamless carbon tubing up to $973 per ton, welded tubing up to $739 per ton, seamless carbon casing up to $701 per ton, and welded casing up to $560 per ton. After climbing to $7.5 billion in 2000, largely due to the strength of the U.S. economy in the late 1990s, the value of U.S. steel and pipe industry shipments fell to $6.6 billion in 2001 due to domestic economic turmoil.
In the United States, the automotive, display fixture, juvenile furniture, and exercise and recreation equipment industries showed healthy increases in demand for steel pipes and tubes throughout the late 1990s, although demand for these products declined substantially when consumer confidence weakened in the early 2000s. Regionally, the Midwest, mountain, and southern states
exhibited high demand, while sales in the Northeast and on the West Coast remained stagnant.
The largest steel pipe and tube producing states in descending order are Pennsylvania, Ohio, Illinois, and California, which together ship 55 percent of total U.S. shipments. New capital expenditures on plant and equipment totaled $181.5 million, an increase of over 50 percent from 1990 levels. The cost of materials totaled $4.8 billion in 2000.
In 1992, the U.S. International Trade Commission and U.S. Commerce Department ruled in favor of many American pipe and tube manufacturers, concluding that foreign countries were dumping their shipments into the U.S. market at less than the cost of production or values sold at home. The countries guilty of dumping in 1992 (with corresponding duties assessed) were Brazil (103.38 percent); South Korea (4.9 to 11.6 percent); Mexico (32.6 percent); Taiwan (19.5 to 27.7 percent); and Venezuela (52.5 percent).
The American steel mill products industry, which includes steel tubes and pipes, exported $13.4 billion worth of goods in 1995, a 44 percent increase over the 1994 level. Imports of foreign steel pipe and tubes totaled $3.2 billion, an increase of 7.3 percent from 1994. Increased competition from inexpensive steel imports throughout the late 1990s and early 2000s prompted the U.S. to begin levying tariffs of up to 30 percent on imports from countries such as China, Japan, South Korea, Russia, Brazil, Australia, and members of the European Union as of March 20, 2002.
Cleveland, Ohio-based LTV Steel Company Inc. led the industry with sales of more than $4.4 billion in 1997. LTV's Steel Tubular Products Co. division, located in Youngstown, Ohio, contributed $300 million to the company's 1998 sales. In December of 2002, Maverick Tube Corporation, based in St. Louis, Missouri, acquired the tubular operations of LTV, which had filed for bankruptcy protection, for $120.2 million.
Babcock and Wilcox Co. of Barberton, Ohio, was another industry leader in the early 2000s. It operated as a subsidiary of McDermott International Inc., which generated $2.3 billion in sales for 2003. To gain protection from mounting asbestos-related liability in the early 2000s, Babcock and Wilcox filed bankruptcy. Other industry leaders included Houston, Texas-based Quanex Corp., with $1.03 billion in sales for its fiscal year ended October 31, 2003; Ameron International Corp. of Pasadena, California, with $600.5 million in 2003 sales; Sandvik Coromant U.S. of Fair Lawn, New Jersey, with $85 million in estimated sales for 2002; and Marmon/Keystone Corp. of Butler, Pennsylvania.
Further Reading
Sacco, John E. "Maverick Tube Completes Buy of LTV Division." American Metal Market, 3 January 2003.
U.S. Census Bureau. "Statistics for Industry Groups and Industries: 2000." February 2002. Available from http://www.census.gov/prod/2002pubs/m00as-1.pdf .
——. "Value of Shipments for Product Classes: 2001 and Earlier Years." December 2002. Available from http://www.census.gov/prod/2003pubs/m01as-2.pdf .
Comment about this article, ask questions, or add new information about this topic: