SIC 2426
HARDWOOD DIMENSION AND FLOORING MILLS
This classification consists of companies that primarily make hardwood dimension lumber and workings there from and other hardwood dimension, semifabricated or ready for assembly; hardwood flooring; and wood frames for household furniture. Companies that primarily make stairwork, molding, and trim are classified in SIC 2431: Millwork; and those making textile machinery bobbins, picker sticks, and shuttles are classified in SIC 3552: Textile Machinery.
NAICS Code(s)
321918 (Other Millwork (including Flooring))
321999 (All Other Miscellaneous Wood Product Manufacturing)
337215 (Showcase, Partition, Shelving, and Locker Manufacturing)
321912 (Cut Stock, Resawing Lumber, and Planing)
Hardwood flooring and furniture components make up the largest shares of output in this industry segment. The remaining output includes many items, such as skis, golf clubs, and tool handles. Wood blocks for bowling pins and textile machinery accessories, rounds or rungs for ladders, and spool blocks and blanks are also produced by this industry.
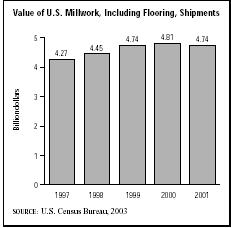
After increasing steadily throughout the late 1990s, the total value of shipments for millwork, including flooring, declined from $4.81 billion in 2000 to $4.74 billion in 2001. Although the hardwood flooring industry remained healthy during the economic recession of the early 2000s, it did face increased competition from laminate products, which were considered more durable and less likely to scratch.
Since the health of this industry is tied closely to housing starts in the United States, the strong economy of the mid- to late 1990s had brought rising revenues. Even when the economy declined in the early 2000s, housing starts remained strong due to record low interest rates. In fact, housing starts reached a 25-year high of 1.84 million units in 2003, according to the National Association of Home Builders. This trend bolstered many segments of the construction industry, including hardwood flooring.
Among other trends propelling the growth in this industry were the tendency for new houses to be bigger than those built in the early 1990s (the average square footage of a new home in 2002 was 2,230, compared to 2,080 in 1990); the growth of interest in restoration and repair; and the increase in popularity of hardwood flooring. Wood flooring reached an industry low in 1982, but in the 1990s the installation of hardwood flooring increased nearly 10 percent. By 2002, a total of 11 percent of new single family homes were built with hardwood flooring.
Oak, beech, birch, maple, and pecan are the species most often used in furniture and flooring manufacturing in the United States. Ash, cherry, poplar, and walnut are also frequently used. Moreover, four types of flooring are commonly made: strip, parquet, plank, and laminated.
Hardwood dimension and flooring generally account for 8 to 10 percent of hardwood lumber exports by value. Canada, Japan, and Taiwan are the most frequent destinations of dimension and flooring exported by the United States. In the late 1990s, about 12 percent of the dimension and flooring used in the United States was imported, with the biggest suppliers being Canada and Japan.
Throughout the late 1990s and early 2000s, wood product imports were expected to increase, especially from Canada. U.S. exports to Asian markets suffered during the Asian financial crisis of the late 1990s; exports were expected to increase as the difficulties in the region wane. China's entrance into the World Trade Organization in 2001 was also expected to offer new export opportunities to the United States.
Lancaster, Pennsylvania-based Armstrong World Industries, formerly Triangle Pacific Corporation, is an industry leader, with 2003 sales of $3.2 billion and nearly 15,200 employees. Armstrong makes hardwood floors under the brand names Bruce, Hartco, and Robbins. The company's cabinet division makes wood cabinets for kitchens and bathrooms with brand names such as Ultrawood, Baseline, and Gemini. Crown Pacific Partners, L.P. of Portland, Oregon, was another industry leader with 2002 sales of $484 million and 769 employees. The company owns mature forests in Washington, Oregon, Idaho, and Montana that, combined, total over 700,000 acres and have a potential for billions of board feet of lumber. In the early 2000s, Crown Pacific filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection while it restructured its debt and streamlined operations.
Several issues may affect the hardwood dimension and flooring industry in the 2000s. Changes in logging and land management regulations could have a major impact, as well as legislation affecting lumber imports or exports. Those changes, coupled with stricter air pollution laws, may drive up the cost of lumber. The industry will most likely remain vulnerable to any changes, good or bad, in the number of housing starts. As long as the low interest rates and strong housing starts of the early 2000s persist, a desire for furniture and flooring is expected to remain strong. An interesting future trend, based primarily on environmental concerns, may be the refurbishing and marketing of "antique" floor and wall boards salvaged from condemned buildings.
Further Reading
National Association of Home Builders. "Housing Facts, Figures, and Trends 2004." Available from http://www.nahb.org/ .
——. "Total Housing Starts for 2003 Highest in 25 Years," 2004 January 21. Available from http://www.nahb.org/ .
U.S. Census Bureau. "Statistics for Industry Groups and Industries: 2000." February 2002. Available from http://www.census.gov/prod/2002pubs/m00as-1.pdf .
——. "Value of Shipment for Product Classes: 2001 and Earlier Years." December 2002. Available from http://www.census.gov/prod/2003pubs/m01as-2.pdf .
Comment about this article, ask questions, or add new information about this topic: